Types of Deployment Strategies –
- Blue/Green Deployment
In this type of deployment strategy, the new version of the software runs alongside the old version. Note that you can also refer to this as red/black deployment strategy in some cases.
Here, the stable or the older version of the application is always blue or red, while the newer version is green or black.
After the new version has been tested and certified to meet all the requirements, the load balancer automatically switches the traffic from the older version to the newer version.

The major advantage of this strategy is that it avails a quick update or rollout of a new application version. However, its main disadvantage is that it is costly because you must run both the new and old versions concurrently. Engineers mostly use this method in mobile app development and deployment.
2. Canary Deployment
In canary deployment, the deployment team sets up the new version and then gradually shifts the production traffic from the older version to the newer version. For example, at a point in time during the deployment process, the older version might retain 90% of all traffic for the software while the newer version hosts 10% of the traffic.
This deployment technique helps the DevOps engineers test the stability of the new version. It uses live traffic from a subset of the end-users at different levels that varies as production occurs.
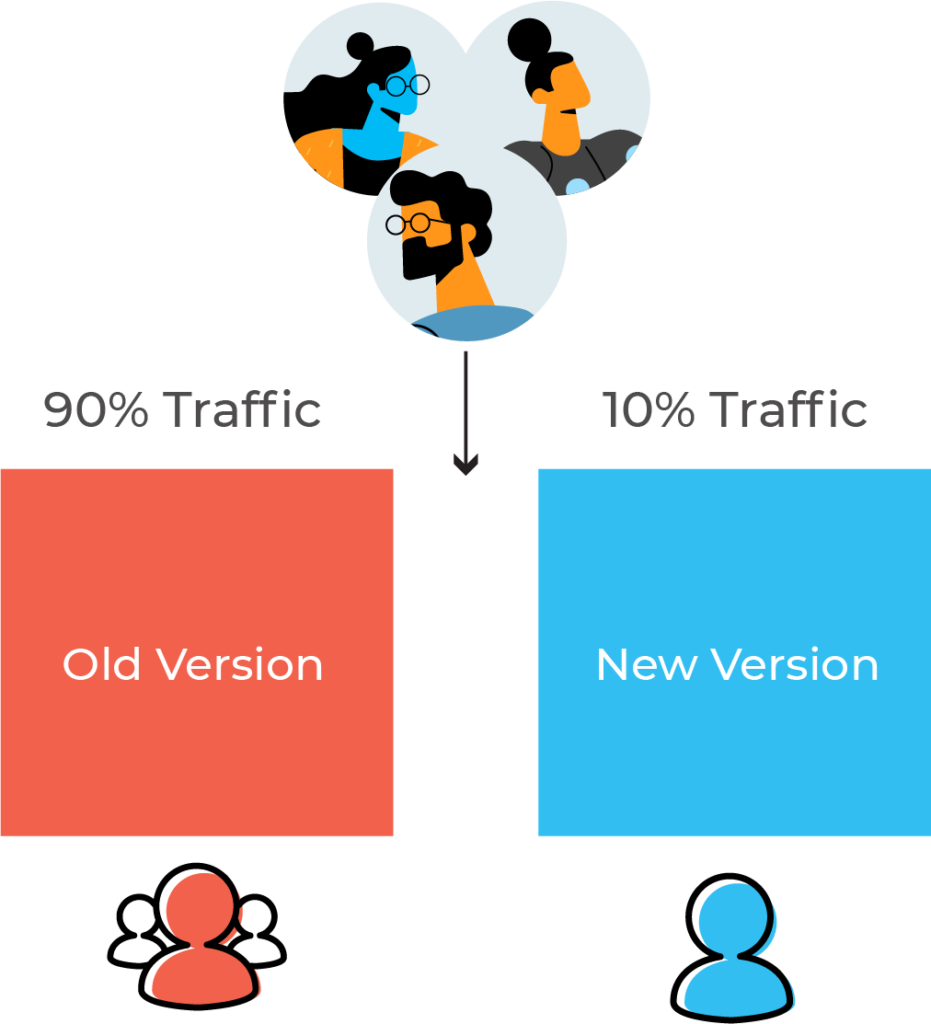
Canary deployment enables better performance monitoring. It also aids in a faster and better rollback of the software if the new version fails. However, it has a slow nature and a more time-consuming deployment cycle.
3. Ramped Deployment
The ramped deployment strategy gradually changes the older version to the new version. Unlike canary deployment, the ramped deployment strategy makes its switch by replacing instances of the old application version with the instances from the new application version one instance at a time. You can also call this method the rolling upgrade deployment strategy.
When developers replace all instances of the older version, they shut down the older version. The new version then controls the whole production traffic.
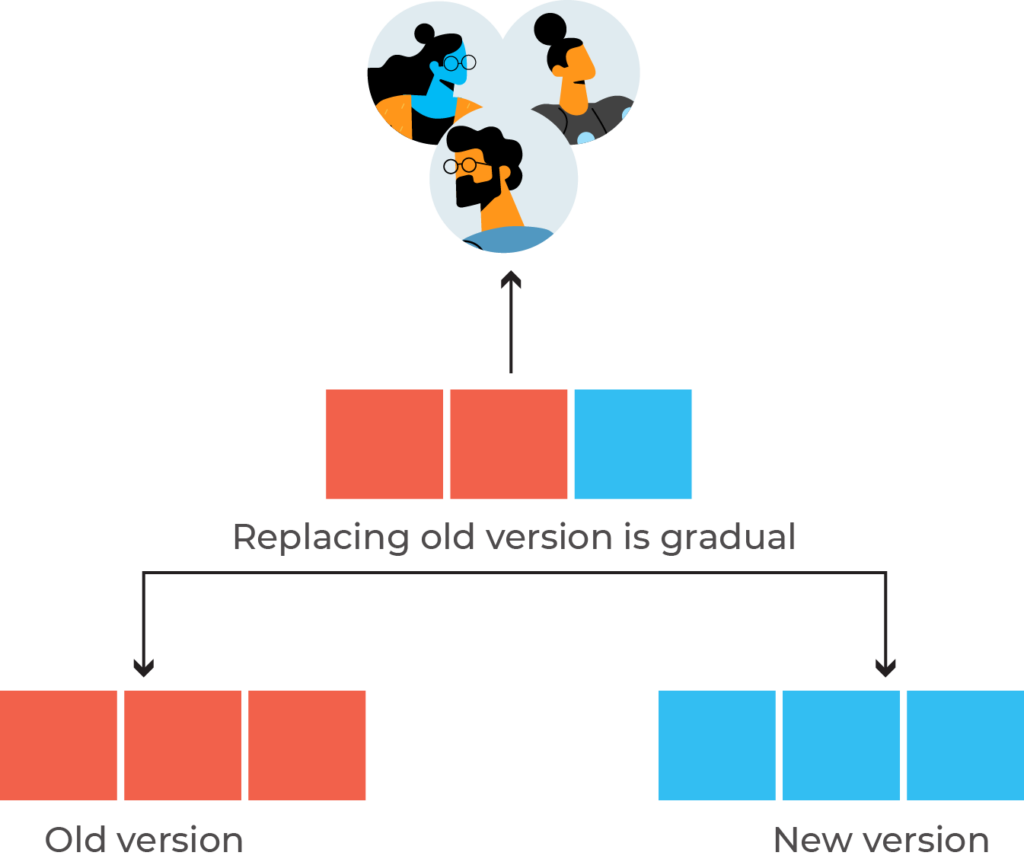
This strategy gives zero downtime and also enables performance monitoring. Nevertheless, the rollback duration is long in case there is an unexpected event. This is because the downgrading process to the initial version follows the same cycle, one instance at a time.