Linux ifconfig –
The command ifconfig stands for interface configurator. This command enables us to initialize an interface, assign IP address, enable or disable an interface. It display route and network interface.
ifconfig
Hostname -i

Get details of specific interface-
ifconfig eth0
Linux traceroute command-
Linux traceroute command is a network troubleshooting utility that helps us determine the number of hops and packets traveling path required to reach a destination. It is used to display how the data transmitted from a local machine to a remote machine. Loading a web page is one of the common examples of the traceroute. A web page loading transfers data through a network and routers. The traceroute can display the routes, IPaddresses, and hostnames of routers over a network. It can be useful for diagnosing network issues.
apt install inetutils-traceroute
apt install traceroute
The above commands will install the traceroute utility on our system. After the successful installation, the output will look like as follows:
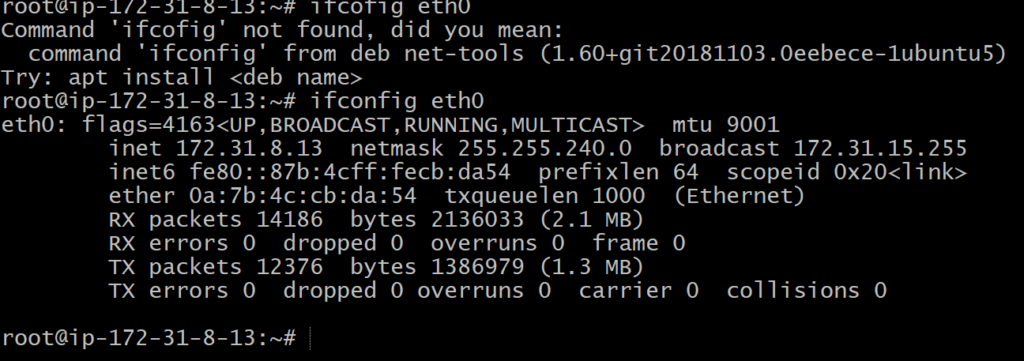
traceroute ygminds.com
Linux tracepath –
It is similar to traceroute command, but it doesn’t require root privileges. By default, it is installed in Ubuntu but you may have to download traceroute on Ubuntu. It traces the network path of the specified destination and reports each hop along the path. If you have a slow network then tracepath will show you where your network is weak.
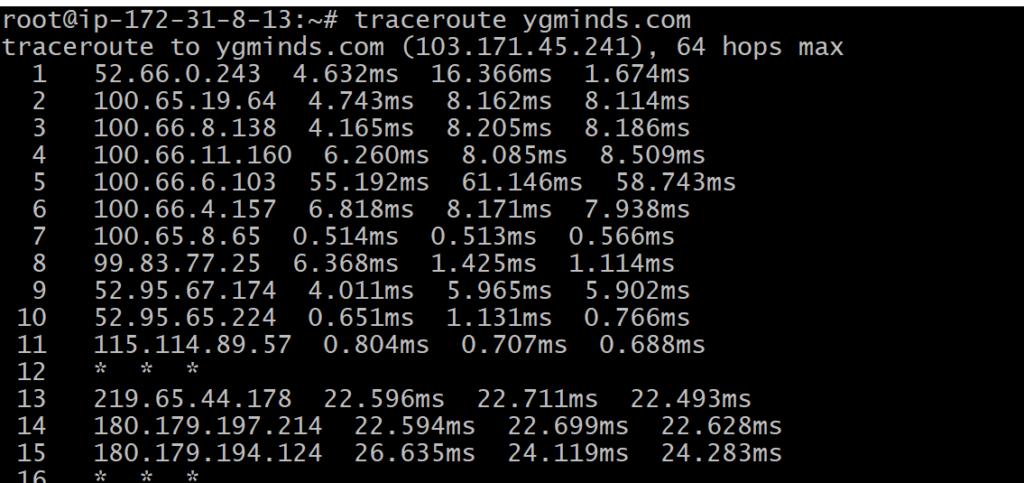
tracepath <destination>
Linux ping Command-
Linux ping command stands for (Packet Internet Groper). It checks connectivity between two nodes to see if a server is available. It sends ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packets to network hosts and displays the data on the remote server’s response. It checks if a remote host is up, or that network interfaces can be reached. Further, it is used to check if a network connection is available between two devices. It is also handy tool for checking your network connection and verifying network issues.
Ping command keeps executing and sends the packet until you interrupt.
The ping command supports various command-line options. But, the basic syntax for the ping command is as follows:
ping <option> <destination>
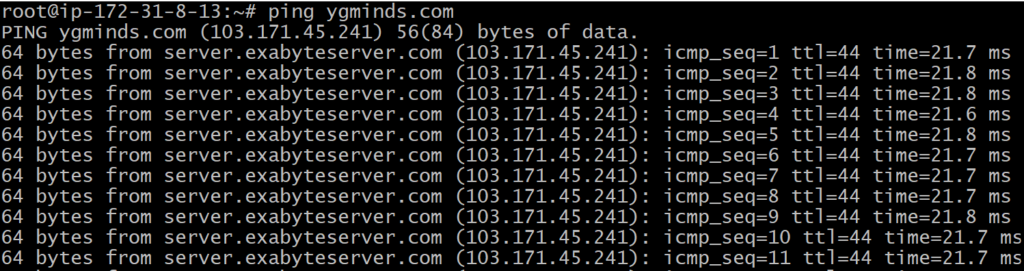
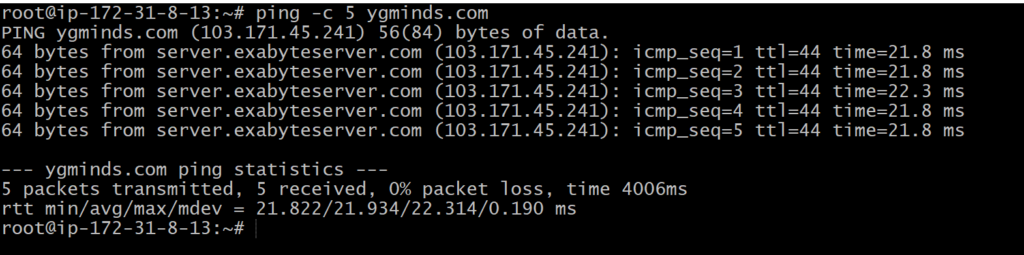
We can limit the number of sent packets by using the ping command. To limit the packet, specify the ‘c’ option followed by the number of packets to be sent. It will be executed as:
ping -c <number> <destination>
Ping -c 5 ygminds.com
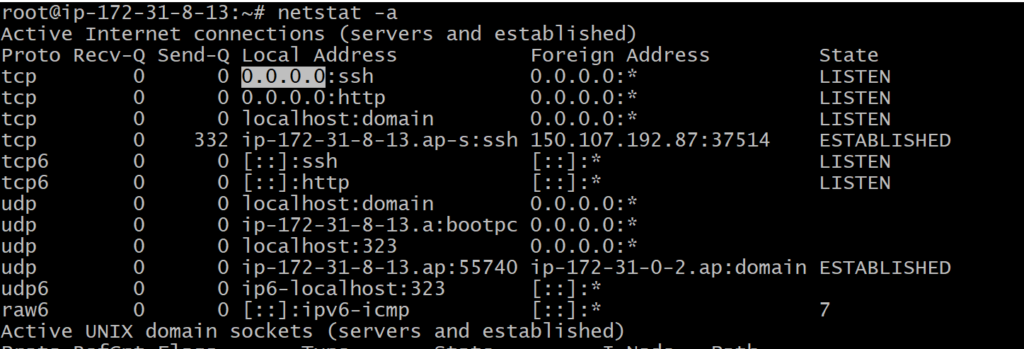
Linux netstat Command-
Linux netstat command stands for Network statistics. It displays information about different interface statistics, including open sockets, routing tables, and connection information. Further, it can be used to displays all the socket connections (including TCP, UDP). Apart from connected sockets, it also displays the sockets that are pending for connections. It is a handy tool for network and system administrators.
apt install net-tools
netstat- a
Linux dig Command (DNS Lookup)-
Linux dig command stands for Domain Information Groper. This command is used for tasks related to DNS lookup to query DNS name servers. It mainly deals with troubleshooting DNS related problems. It is a flexible utility for examining the DNS (Domain Name Servers). It is used to perform the DNS lookups and returns the queried answers from the name server. Usually, it is used by most DNS administrators to troubleshoot the DNS problems. It is a straightforward tool and provides a clear output. It is more functional than other lookups tools.
The dig command supports plenty of command-line options. Additionally, it facilitates batch mode, which is useful for accessing the lookup requests from a file. If it is not specified to the dig command to query a specific name server, it will access each of the servers from “/etc/resolv.conf.” The dig without any command-line options will perform an NS query for “.” (the root).
Query a Domain name
dig ygminds.com

Linux nslookup –
This command is also used to find DNS related query.
nslookup <domainName>