Filesystem hierarchy standard describes directory structure and its content in Unix and Unix like operating system. It explains where files and directories should be located and what it should contain.
The Root Directory
All the directories in the Linux system comes under the root directory which is represented by a forward slash (/). Everything in your system can be found under this root directory even if they are stored in different virtual or physical devices.
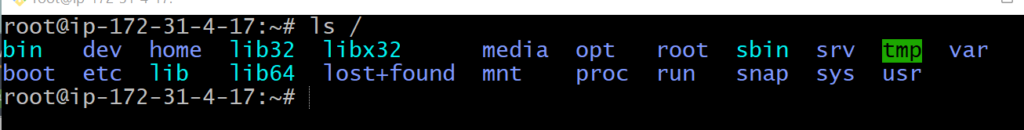
Linux Directories
We have categorize the directories according to the type of file as given below:
| Directory type | Types of files stored |
| Binary directories | Contains binary or compiled source code files, eg, /bin, /sbin, etc. |
| Configuration directories | Contains configuration files of the system, eg, /etc, /boot. |
| Data directories | Stores data files, eg, /home, /root, etc. |
| Memory directories | Stores device files which doesn’t take up actual hard disk space, eg, /dev, /proc, /sys. |
| Unix System Resources | Contains sharable, read only data, eg, /usr/bin, /usr/lib, etc. |
| Variable directories | Contains larger size data, eg, /var/log, /var/cache, etc. |
| Non-standard directories | Directories which do not come under standard FHS, eg, lost+found, /run, etc. |
WINDOWS –
Linux –
