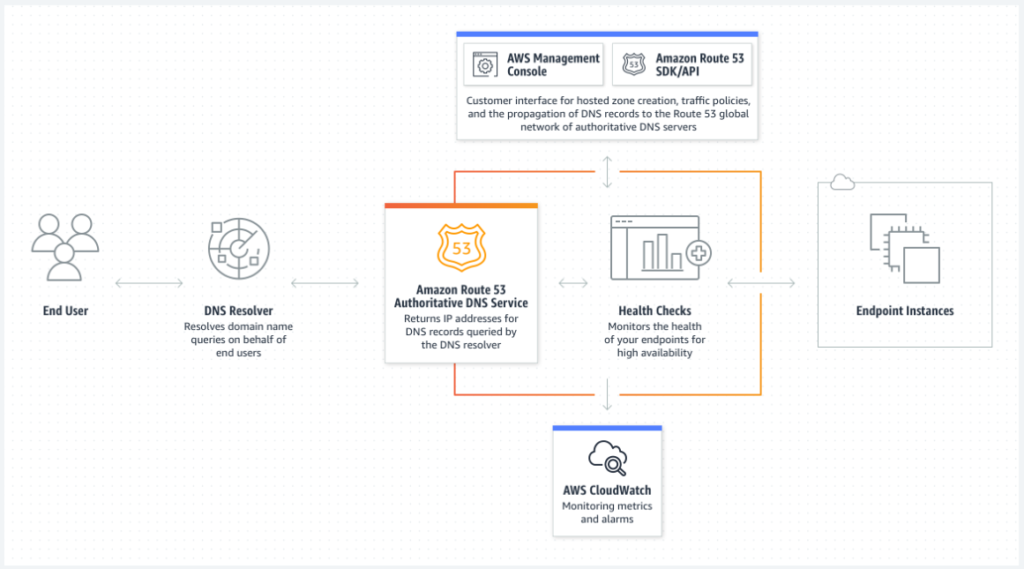
Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service. Route 53 connects user requests to internet applications running on AWS or on-premises.
- DNS is Domain name system.
- It helps resolve Domain name to IP address.
- This works on port number 53, hence this DNS related service which is provided by Amazon is called as Route 53.
- The Domain Name System is the hierarchical and decentralized naming system used to identify computers, services, and other resources reachable through the internet or other internet protocol networks.
- The resource records contained in the DNS associate domain names with other forms of information
Route 53 serves main 4 functions:-
- DNS management
- Traffic Management
- Availability monitoring
- Domain registration
- Here we can create and register our own domains.
- This is not free and the price of the domains depends upon what type of domain we are taking, .com, .NET, .org etc.
- Here the domain which we are trying to create or register should be available.
- Route 53 also acts as a registrar.
- A registrar is where website are registered. Other registrar examples are godaddy.com etc.
- A registrar also tells us that whether the domain is available or not, and also gives us other options.
- One of the major use of route 53 is DNS management.
- It helps route traffic to the resources for your domain, also the domain can be inside our AWS account or outside with any other registrar.
- Route 53 sends automated request to our resources over the internet to a resource to verify that the server is reachable or not.
- You can also choose to receive notifications when a resource becomes unavailable and choose to route traffic away from unhealthy resources.
Some important concepts of Route 53
- Hosted zones –
- A hosted zone is an Amazon Route 53 concept.
- A hosted zone is traditional DNS zone file; it represents a collection of records that can be managed together, belonging to a single parent domain name.
- Basically a hosted zone is a container that holds information about how we want to route traffic for a domain and a subdomain.
- When we buy a domain from AWS we don’t need to create a hosted zone and name servers everything is created automatically.
- There are 2 types of hosted zones, public and private.
- A Route 53 hosted zone is a collection of records for a specified domain.
- You create hosted zone for a domain and then you create records to tell the domain name system how you want traffic to be routed for the domain.
- Basically hosted zone is a container that holds information about how you wants to route traffic for a domain and its subdomains.
- You can create public internet hosted zone or private internal DNS hosted zones.
- For each public hosted zone that you create Amazon route 53 automatically creates a name server NS record and a start of authority SOA record don’t change this records.
- Route 53 automatically creates a name server NS record with the same name as you are hosted zone.
- At least the four name server that are the authoritative name servers for your hosted zone.
- Do not add change or Delete name servers in this record.
- Name servers –
- Nameservers help connect URLs with the IP address of web servers. Nameservers are an important part of the Domain Name System (DNS), which many people call the “phone book of the Internet”.
- Usually we have 4 name servers which will have all the server info, for each hosted zone and they will be unique to the account.
- When someone uses the browser to access our website these name servers inform the browser where to find our resources.
- Records and types of record sets –
- DNS records are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
- Name server records identifies the 4 name servers that you give to your registrar on your DNS service so that DNS is routed to route 53 name server.
- SOA – every single hosted zone has one and only one SOA (start of authority record) at the beginning of the zone.
- This is not an actual record it just holds the info of who the owner is and its email.
Route 53 performs 3 main functions
- Register a domain
- As a DNS it routes internet traffic
- Check the health of your resources
In case, you choose to use Route 53 for all three functions, perform the steps in this order:
1. Register domain names:
Your website needs a name, such as example.com. Route 53 allows you to register a name for your website or web application. This is a domain name.
2. Route internet traffic to the resources for your domain:
When a user opens a web browser and inscribes your domain name (example.com) or subdomain name (acme.example.com) in the address bar, Route 53 assists connect the browser with your website or web application.
3. Check the health of your resources:
Route 53 makes automatic calls to a resource, such as a web server, across the internet to ensure that it is accessible, available, and functioning. You may also opt to be notified when a resource becomes inaccessible, as well as to redirect internet traffic away from harmful resources.
- Route 53 sends automatic request over the internet to a resource can be web server to verify that the server is reachable functional or available.
- Also you can choose receive notifications when a resource become unavailable and choose to route internet traffic away from unhealthy resources.
- You can use route 53 for any combination of these functions.
- For example you can use route 53 port to register your domain name and to route internet traffic for the domain.
- Or you can use route 53 to route internet traffic for a domain that you register with another domain register.
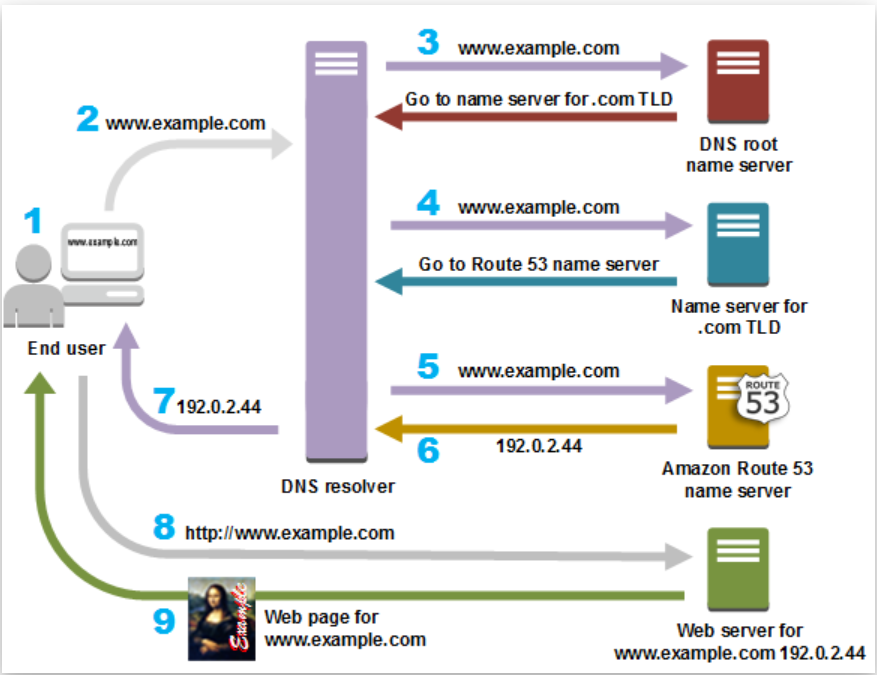
How Does Route 53 Work?
- A user opens a web browser and sends a request for example.com
- The request from example.com is routed to a DNS resolver, which is usually managed by the Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- The ISP DNS resolver forwards the request from example.com to a DNS root name server.
- The DNS resolver forwards the request from example.com again, this time to one of the top-level domain (TLD) name servers of .com domains. The .com domain name server responds with the names of the four Route 53 name servers associated with the example.com domain. The DNS resolver caches the four Route 53 name servers for future use.
- The DNS resolver chooses a Route 53 name server and forwards the request from example.com to that Route 53 name server.
- The Route 53 name server looks for the record example.com in the hosted zone site.com, gets its value, such as the alias of Amazon CloudFront distribution in the case of simple routing.
- The DNS resolver finally has the right route (CloudFront IP) the user needs and returns the value for the user’s web browser.
- The web browser sends a request from example.com to the IP address of the CloudFront distribution.
- The example CloudFront distribution returns the web page from cache or origin server for example.com to the web browser.
When you register a domain with route 53
- The service automatically makes itself the DNS service for the domain by doing the following-
- It creates that has the same name as your domain.
- It assign a set of four name servers to the hosted zone unique to the account.
- When someone use a browser to access you are website this name servers inform the browser when to find your resources such as a web server or an Amazon is S3 bucket.
- It gets the name servers from the hosted zone and ads them to the domain.
AWS supports
1. Generic top level domains
2. Geographic top level domains
Registering a domain with route 53
- You can register a domain with route 53 if the TLD is included on the supported TLD list.
- If the TLD is not included you can’t register the domain with Route-53.
Using route 53 as your service
- You can use route 53 as the DNS service for any domain even if they TLD for the domains is not included on the supported TLD list.
Note:- each Amazon route 53 account is limited to maximum of 500 hosted zones and 10000 resource record sets per hosted zone you can increase this limit by requesting to AWS.
Steps to configure Route-53
- This domain can be Route 53, or another DNS register but then you connect you are domain name in that register to Route 53.
- Create hosted zone on Route 53, this is clone automatically if you registered your domain using Route 53.
- Inside the hosted zone you need to create record sets.
- Delegate to Route 53
- This step connects everything and make it works.
- Connect the domain name to the route 53 hosted zone this is called delegation.
- Update you are domain register with the correct name servers for your route 53 hosted zone.
- No other customer hosted zone will share the delegation set with you.
- Doing this means route 53 DNS service will be serving DNS traffic for the domain of the hosted zone.
- If you register you are domain with different registrar, you need to configure the route 53 NS service list in your registrar DNS database for your domain
- If you are using another domain provider and you did all the changes
- When you migrate from one DNS provider to another for an existing domain this change can take up to 48 hours to be effective.
- This is because name server DNS records are typically catches across the DNS system globally on the internet for up to 48 hours TTL periods.
Transferring domain to route 53
- You can transfer a domain to route 53 if the TLD is included on the following list
- If the TLD is not included you can’t transfer the domain to route 53.
- For most TLD you need to get an authorization code from the current registrar to transfer a domain.
- When you create hosted zone Amazon Route 53 automatically creates a name server (NS) records and start of authority records (SOA) for the zone.
- The NS records identifies the four names servers that you give your register or you are DNS service so that DNS Queries are routed to route 53 name servers.
- By default route 53 assign a unique set of four name servers (known collectively as a delegation set) to each hosted zone that you create….
- E.g. : ns-1337 awsdns-39.com
Route 53 as Your Authoritative DNS
- Once you update the route 53 NS setting with you are domain register to include the route 53 name servers route 53 will be responsible to respond to DNS queries for the hosted zone.
- This is true whether you do have a functioning website or not.
- Route 53 will respond with information about the hosted zone whenever someone types the associated domain name is a web browser.
- You can create more than one hosted zone with the same name and add different records to each hosted zone.
- Route 53 assigns four name servers to every hosted zone.
- The name servers are different for each of them.
- When you update you are registers name server records be careful to use the route 53 name servers for the correct hosted zone the one that contains the records that you want route 53 to use when responding to queries for your domains.
- Route 53 never returns value for records in other hosted zones that have the same zone.
Route 53 Hosted zone default Entries–
- Inside the hosted zone by default you have two entries.
- NS entry:- Contains the unique Sets of name servers for this Hosted zone.
- SOA entry:- Contains information about the hosted zone.
- If you are currently using another DNS service and you want to migrate to Amazon route 53.
- Start by creating a hosted zone a doubt 53 automatically a sign the delegation sets, the four name servers.
- To ensure that the DNS routes queries for you are domain to the route 53 name servers.
- Update your registers on you are DNS service NS records for the domain to replace the current name servers with the names of the four route 53 name servers for your hosted zone.
- The method that you use to update the NS records depends on which register or DNS service you are using.
- Some register only allow you to specify name servers using IP address they don’t allow you to specify fully qualified domain names
- If you are register requires using IP address you can get the IP address for your name servers using the DIG utility for Mac Linux and NS look up for Windows.
Transferring a domain between accounts within AWS-
1. Transferring a domain to different AWS account - If you registered a domain using one AWS account and you want to transfer the domain to another AWS account you can do so by contacting the AWS support centre and requesting the transfer.
- Migrating a hosted zone to different account.
- If you are using route 53 as the day and S service for the domain route 53 does not transfer the hosted zone when you transfer a domain to a different AWS account
- If domain registration is associated with one account and the correspondence hosted zone is associated with another account neither domain registration nor DNS functionality is affected
- The only effect is that you will need to sign into the route 53 console using one account to see the domain and signed in using the other account to see the hosted zone.
2. Support DNS record types by route 53-
- A Record- Address Record – Maps domain name to IP address www.ygminds.com IN A 5:5:5:5
- AAAA Record- IPv6 address record Maps domain name to an IPv6 addressv www.ygminds.com IN AAAA 2002:b768::1
- CNAME Record- Maps an alias to a host name Web IN CNAME www.ygminds.com
- NS Records- Name server record used for delegating zone to a name server ygminds.com IN nsi ygminds.com
- SOA Records- Start of Authority Record
- MX Records- Mail exchange – defines where to deliver mail for user @ a domain name.
- NS records defines which name server is authoritative to a particular zone or domain name and point you to other DNS servers-
- A/AAAA are called host records, like business cards.
- CNAME is an alternative record or an alias for another record
- Helpful in direction or if you want to hide details about you are actual servers from the users
Start of Authority Records (SOA)
- Every single zone has won and only one so a resource record at the beginning of the zone.
- It is not an actual record it includes the following information.
- Who the owner is email for the domain.
- The authoritative server
- The serial number which is incremental with changes to the zone data.
- The refreshing time/cycle into and the TTL.
C NAME Record types–
- CNAME value element is the same format as a domain name.
- The DNS protocol does not allow you to create a CNAME record for the top not of a DNS namespace also known as the zone Apex or (root domain).
- You cannot create a CNAME Record for ygminds.com
- However you can create CNAME records for www.ygminds.com support ygminds.com and so on
- In addition if you create a CNAME record for a subdomain you cannot create any other records for that sub domain.
Routing Policies:
- Simple routing policy
- Use for a single resource that performs a given function for your domain, for example, a web server that serves content for the example.com website. You can use simple routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
Failover routing policy:
- Use when you want to configure active-passive failover. You can use failover routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
- Fail over routing lets you route traffic to a resource when the resource is healthy if the main resource is not healthy then route traffic to a different resource.
- The primary and secondary records can row traffic to anything from an Amazon S3 bucket that is configured as a website to a complex tree of records.
- Failover Routing policy is applicable for public hosted zone only.
Geolocation routing policy :
- Use when you want to route traffic based on the location of your users. You can use geolocation routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
- Geo location routing lets you choose the resources that servers you are traffic based on the geographic location of you are users i.e. the location that DNS queries originate from.
- For e.g. You may have person in Europe and Asia now you want users in the Asia to be served in the Asia and those in Europe to be served by servers in Europe.
Geo-proximity routing policy :
- Use when you want to route traffic best on the location of your resources and optionally shift traffic from resources in one location to resources in another.
- You can also optionally choose to route more traffic or less to a given resource by specifying a value known as ABI as BIA s expand or shrinks the size of Geographic region from which traffic is routed to a resource
- Benefits:
- You can localize you are content and present some or all of your website in the language of your users.
- You can also use Geo location routing to restrict distribution of content to only the locations in which you have distribution rights.
- You can specify Geographic locations by continent by country or by state in the United States.
- If you create separate records for overlapping Geographic regions for example one record for North America and one for Canada priority ghost to the smallest Geographic region.
- Geolocation Works By mapping IP address to locations however some IP address are not map to geographic location
Latency routing policy
- Use when you have resources in multiple AWS Regions and you want to route traffic to the region that provides the best latency. You can use latency routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
- If you are application is hosted in multiple Amazon easy to regions you can improve performance for your users by serving they are request from the Amazon ec2 region that provide the lowest latency.
- To use latency based routing you create latency records for your resources in multiple ec2 regions.
- When Amazon route 53 receives a DNS query for your domain or sub domain.
- It determines which Amazon easy to region you have create latency records for.
- Determine which regions gives lowest latency to users.
- Then select a latency record for that region, For e.g.- suppose you have ELB in US East and in Asia Pacific Mumbai region.
- You created a latency records for each Load Balancer
- Here’s what happens when a user in London enters the name of your domain in a browser.
- DNS routes the request to a route 53 name server
- Route 53 refers to its data on latency between London and the Mumbai region and between London and the north Virginia.
- Latency is lower between London and N Virginia, route 53 respond to the query with the IP address for the N Virginia LB.
IP-based routing policy
- Use when you want to route traffic based on the location of your users, and have the IP addresses that the traffic originates from.
Multivalue answer routing policy
- Use when you want Route 53 to respond to DNS queries with up to eight healthy records selected at random. You can use multivalue answer routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
- Multi value answer routing lets you configure Amazon route 53 to return multiple values such as IP addresses for your web servers in response to DNS queries you can specify multiple values for almost any record but multi value answer routing also lets you check the health of each resource so route 53 returns only values for healthy resources it is substitute for A Load Balancer.
- But the ability to return multiple health check cable IP addresses is a way to use DNS to improve availability and load balancing.
Weighted routing policy
- Use to route traffic to multiple resources in proportions that you specify. You can use weighted routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
- Weighted routing policy lets you associate multiple resources with a single domain name or subdomain name and choose how much traffic is routed to each resource.
- This can be useful for a variety of purposes including load balancing and testing new versions of software.
- Weighted can be assigned any number from 1 to 255.
- Weighted routing policy can be applied when there are multiple resource that perform the same function for example web server serving the same website.
- To configure wedded routing you create records that have the same name and type for each of your resource.
For example suppose for www.tz.com has three resource record sets with weight of 1 (20%) and 3 (60%)(sum=5) - On average route 53 select each of the list two resource records set on 5th of the line and returns the third resource record set three-fifth of the time.
Benefits of Route 53